Lightweight construction: a new era
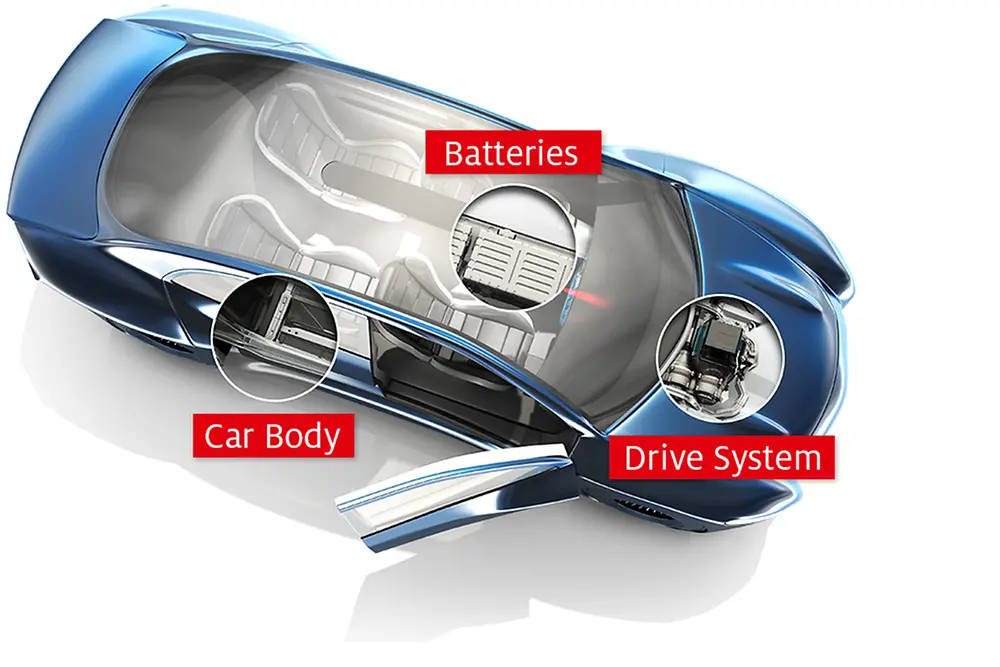
The car of the future will be electric – that much is clear. However, manufacturers still face some major challenges before comprehensive and emissions-free electromobility becomes a reality. In particular, the complex battery technology, weighing 500 kilograms on average, changes vehicle construction and design. This is why new, lightweight concepts are needed to enable final breakthrough of electric cars.
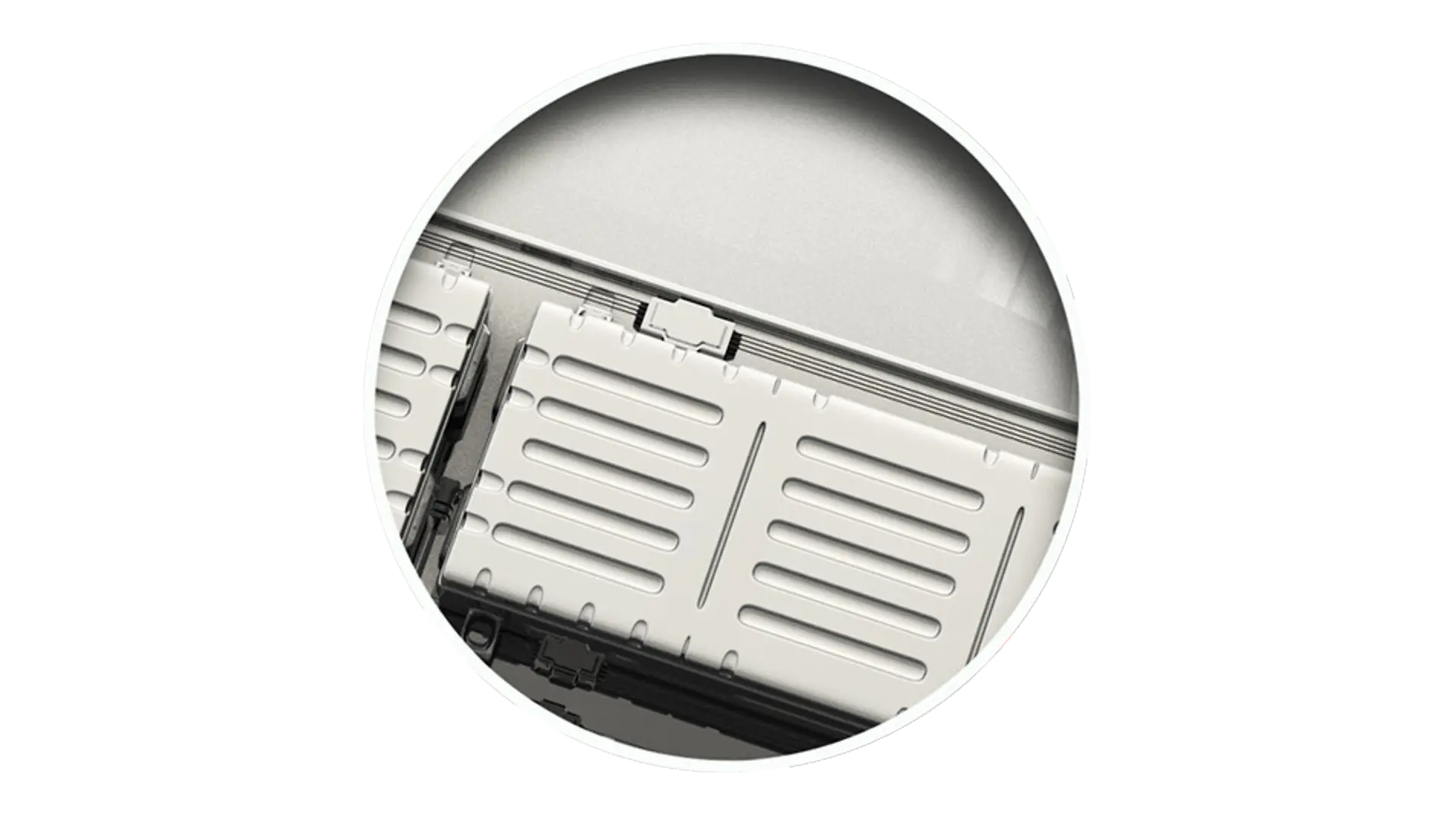
Powerful lithium-ion batteries that serve as energy storage systems are the central elements of an electric car. To enable a high cruising range, a large number of batteries are built into the vehicle underbody as so-called battery packs. Depending on the model, these may weigh up to 800 kilograms. This additional weight, in turn, undermines the car’s driving range and performance. The technology also calls for new safety solutions to protect batteries from external damage and overheating, especially in the event of a crash.
Adhesive technologies pave the way for lightweight construction
Powerful adhesives, sealants and functional coatings today already make a modern car up to 15 percent lighter than before. Their importance will grow even further in future generations of hybrid and electric vehicles, because these materials enable advanced lightweight construction concepts for batteries, car bodies and powertrain systems. They allow manufacturers to develop new designs and constructions that will help making electric cars safer, more sustainable and more efficient.

Safer
Using lithium-ion batteries as energy storage increases the requirements for safety and passenger protection in the event of a crash. Thermal adhesives ensure optimal temperature management and prevent overheating. Structural adhesive solutions enable compact construction methods for the batteries and thus help to reduce their weight. Additionally, sealants and functional coatings protect the battery pack from external influences. They prevent leaks and contribute to the durability and improved protection of electric cars.
Manufacturers have continually enhanced the active and passive safety of their cars over time. Battery technology now confronts them with new challenges due to its high energy density. Electric cars must be designed in such a way that, in an accident, the batteries remain intact to protect passengers and rescue teams from risks like high voltage tension or leaking substances.
High-performance structural foams make it possible to use fiber-reinforced composites for the fitting of battery packs in the vehicle underbody. They don’t just ensure a durable and secure hold between the components and the car body, but also allow more compact constructions. Automakers thereby increase the crash safety of their electric vehicles, while also being able to use lighter materials and reduce the total weight thanks to hybrid structures.
Heat-conductive pastes, heat-dissipation materials and gap-filling thermal compounds otherwise known as gap pads are also among the invisible but indispensable components for lithium-ion batteries. They handle the critical heat management that ensures a constant operating temperature of 15 to 55 degrees Celsius. In doing so, they boost performance and simultaneously prevent the batteries from overheating.

More Sustainable
An electric vehicle’s weight influences its energy consumption and driving range. Manufacturers therefore use lightweight construction materials in the design of the car body and components. Adhesives are an integral part of these concepts. They alone make it possible to combine materials like steel with aluminum and composites. However, they don’t just reduce the weight of modern cars by up to 15 percent – thereby making them more sustainable – they also enhance safety, durability and as well as the overall driving experience.
The lighter a car is, the lower its consumption. Automakers have been moving towards lightweight construction for years as part of their efforts to reduce vehicles’ carbon emissions. In the case of electric cars, they face the challenge of compensating for the added weight of the batteries. Although these vehicles don’t emit any greenhouse gases, their weight still influences their energy consumption and cruising range.
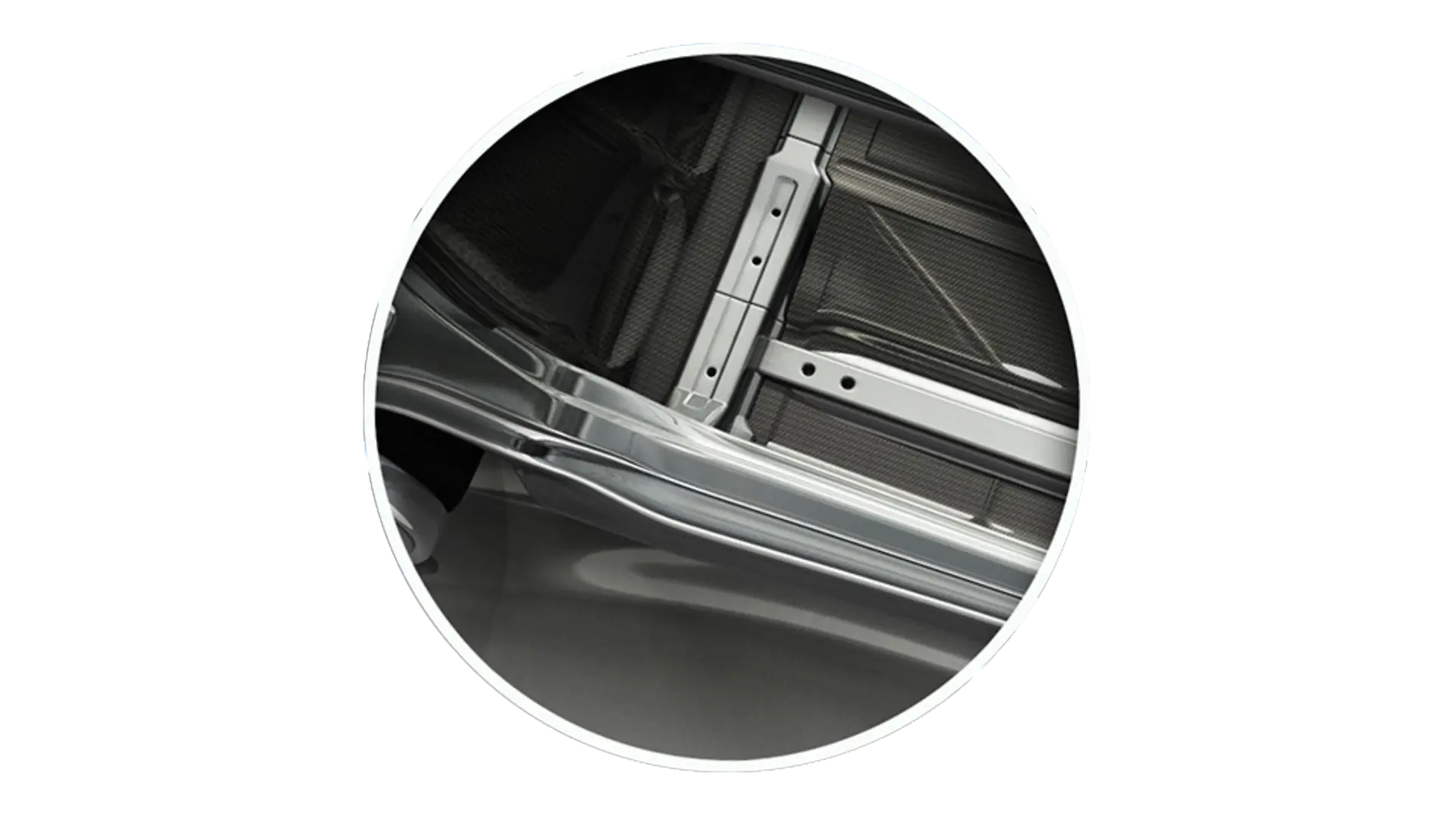
In modern car construction, structural adhesives have long since become indispensable – be it in the roof, doors or windshield. They are replacing traditional technologies like bolting or welding, because they enable a stronger and more durable bond between car parts and components. At the same time, they give manufacturers a lot of freedom when it comes to design and materials. Only adhesives and their flexible bonding properties allow the combination of modern lightweight construction materials such as aluminum, magnesium and composites with steel – without sacrificing either performance or comfort.
To reduce the vehicle weight further, many automakers today use thinner materials for doors and roofs. Here, too, structure-strengthening adhesive solutions play an important role: They increase stability in critical parts of a car and ensure that the lightweight construction meets all safety standards, including in a crash.
weight reduction with modern adhesive technologies

More Efficient
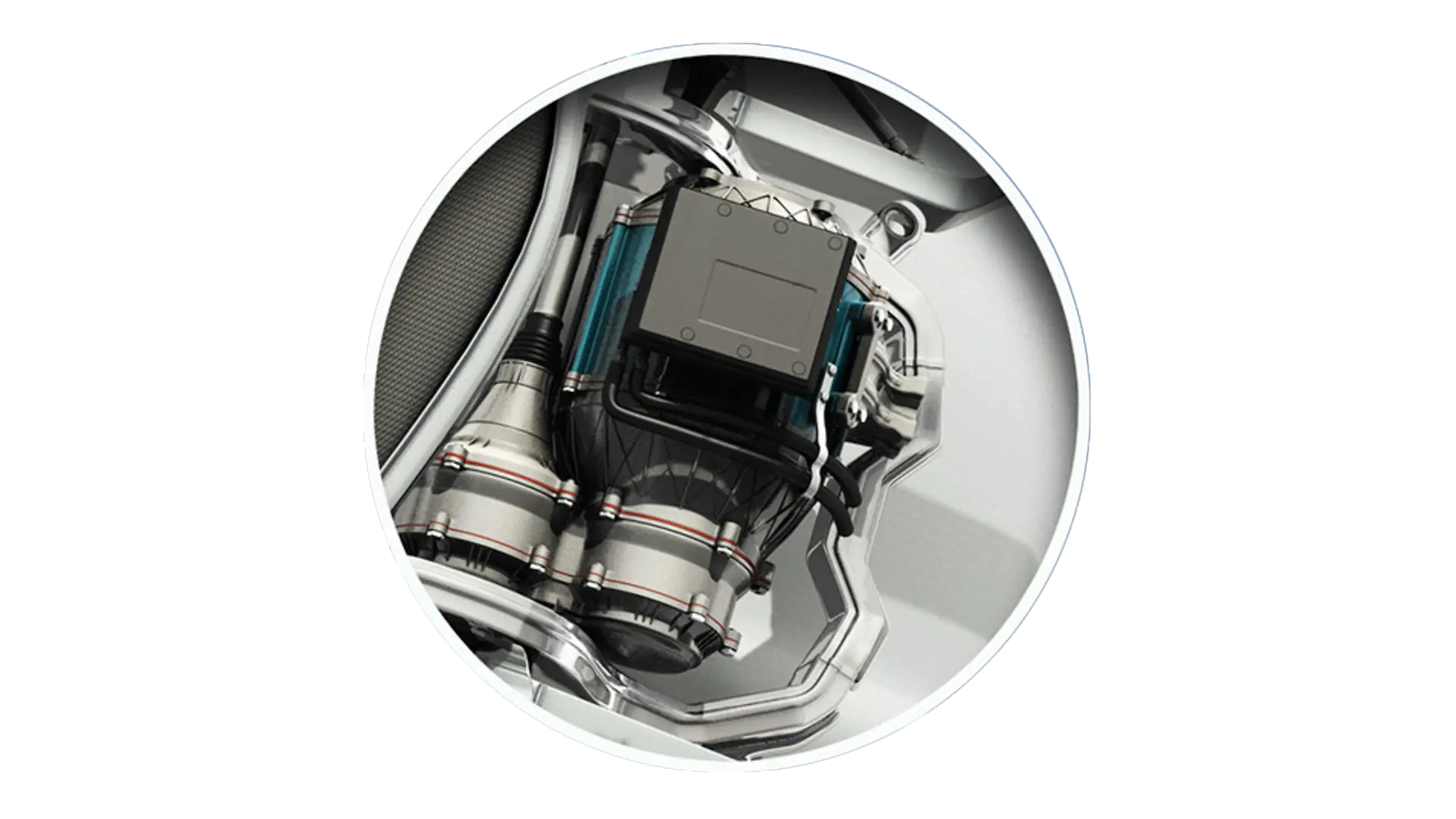
Electric drive units offer a dynamic driving experience with higher torque. New adhesive solutions in the engine, gearbox and electronics contribute to higher durability and operational safety. They also allow an optimized design of the powertrain system, as well as making electric cars lighter and more efficient.
Compared to combustion engines, electric cars are revolutionizing the driving experience. They are particularly appreciated for their quiet, dynamic and uninterrupted drive. This is usually provided by two electric engines, which are connected to a strong electric drive axle along with the power electronics and the gearbox. Adhesives increase the service life of parts and components throughout the powertrain. They also make it possible to use new, lighter materials and help manufacturers to implement more compact construction methods for higher efficiency.
Bringing efficient electromobility onto the streets quickly and effectively requires fresh ideas and new concepts. Strong partnerships, materials science and engineering know-how need to be combined to find new solutions to the challenges posed by this technology. Under the banner of “The Mobility Alliance”, Henkel is working together with RLE International to develop new lightweight construction concepts for the automotive industry – to make the future look lighter.
“The combination of materials expertise and engineering know-how is the key to new solutions in the field of electromobility.”
Christian Kirsten, Global Head of the Transport and Metal business area at Henkel